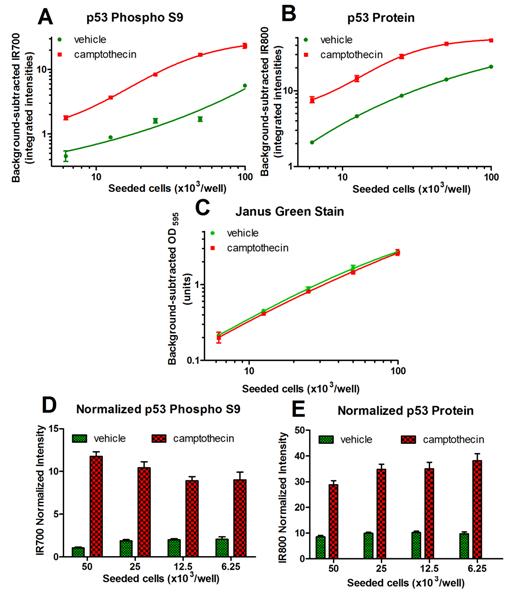
The data is presented as mean +/- SEM. Camptothecin treatment induced an increase in both p53 phospho S9 levels (A, D) and total p53 protein levels (B, E). Note that the Janus Green-normalized intensities are not constant with amount of seeded cells for both analytes (D, E). This is caused by imperfect IR signals linearity with cell dilution (A, B). To eliminate this effect, all samples (wells) should have similar amount of cells.
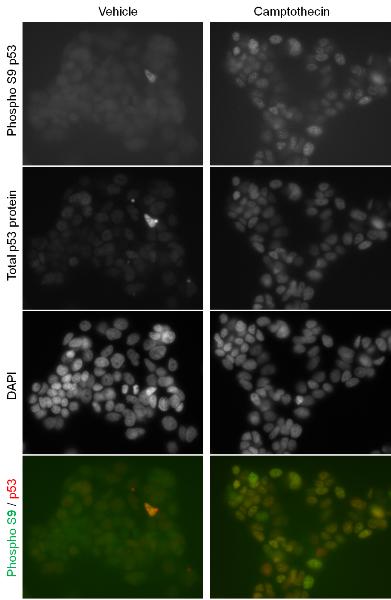
Primary antibodies used in this assay kit were validated by staining MCF-7 cells treated with camptothecin or vehicle (as in Figure 1) and imaged by fluorescent microscopy. (1) Mostly nuclear localization of both p53 phospho S9 and total p53 protein signals. (2) Increase in both p53 phospho S9 and total p53 protein signals upon camptothecin treatment.
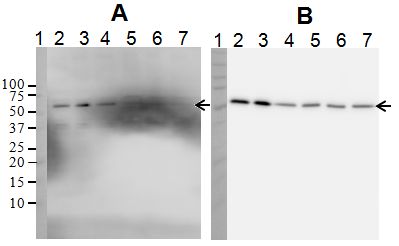
Extracts of Hek293T cells (20 µg/lane) were treated with vehicle (lane 2) or etoposide (lane 3). Extracts of Hek 293T cells (induced with etoposide, 8 µg/lane) were treated with increasing concentrations of lambda protein phosphatase (lane 5, 400x diluted; lane 6, 100x diluted; lane 7, 25x diluted) or left untreated (lane 4). Samples were analyzed by Western blotting using the rabbit p53 Phospho S9 Antibody (A) or the mouse Total p53 Protein Antibody (B). Note the sensitivity of the p53 phospho S9 signal to treatment with lambda protein phosphatase and resistance of the total p53 protein signal to this treatment.


