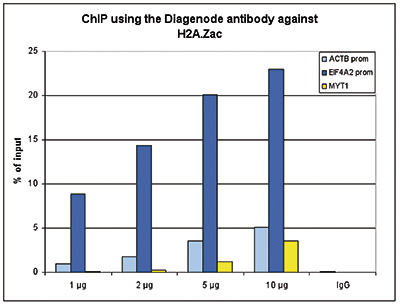
 Figure 1. ChIP results obtained with the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac
Figure 1. ChIP results obtained with the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac ChIP assays were performed using HeLa cells, the Diagenode antibody against H2A.Zac (Cat. No. pAb-173-050) and optimized primer pairs for qPCR. ChIP was performed on sheared chromatin from 1 million HeLaS3 cells using the “Auto Histone ChIP-seq” kit (Cat. No. AB-Auto02-A100) on the SX-8G IP-Star automated system. A titration of the antibody consisting of 1, 2, 5 and 10 μg per ChIP experiment was analysed. IgG (2 μg/ IP) was used as negative IP control. QPCR was performed using primers specific for the promoters of the ACTB and EIF4A2 genes, used as positive control targets and for the coding region of the MYT1 gene, used as a negative control target. Figure 1 shows the recovery (the relative amount of immunoprecipitated DNA compared to input DNA). These results confirm the observation that acetylation of H2A.Z is present at active promoters.
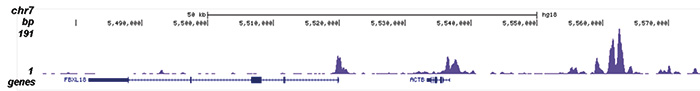
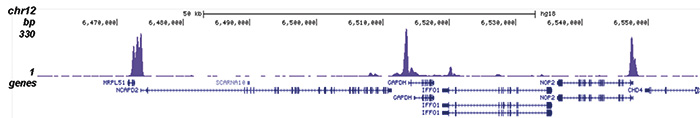
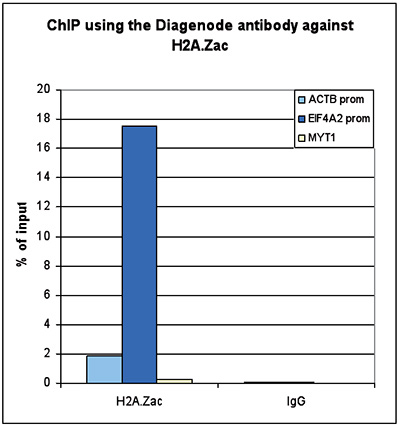 Figure 2. ChIP-seq results obtained with the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac
Figure 2. ChIP-seq results obtained with the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac ChIP was performed with 1 μg of the Diagenode antibody against H2A.Zac (Cat. No. pAb-173-050) on sheared chromatin from 1 million HeLaS3 cells using the “iDeal ChIP-seq” kit (Cat. No. AB-001-0024). IgG (2 μg/IP) was used as a negative IP control. The IP’d DNA was analysed by QPCR as described above (figure 1A). The IP’d DNA was subsequently analysed with an Illumina Genome Analyzer. Library preparation, cluster generation and sequencing were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The 36 bp tags were aligned to the human genome using the ELAND algorithm. Figure 1 shows the peak distribution along the complete sequence and a 600 kb region of the X-chromosome (figure 1B and C) and in 100 kb regions surrounding the EIF4A2, ACTB and GAPDH genes (figure 1D, E and F). These results clearly show an enrichment of the H2A.Z acetylation at the promoters of active genes
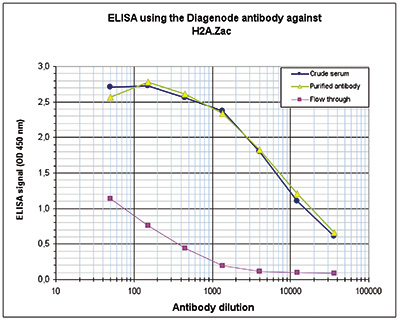
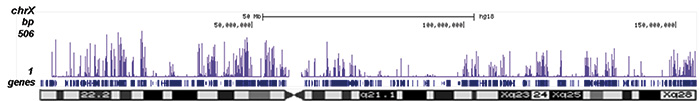 Figure 3. Determination of the antibody titer
Figure 3. Determination of the antibody titer To determine the titer of the antibody, an ELISA was performed using a serial dilution of the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac (Cat. No. pAb-173-050), crude serum and flow through in antigen coated wells. The antigen used was a peptide containing the histone modifications of interest. By plotting the absorbance against the antibody dilution (Figure 3), the titer of the purified antibody was estimated to be 1:8,800.
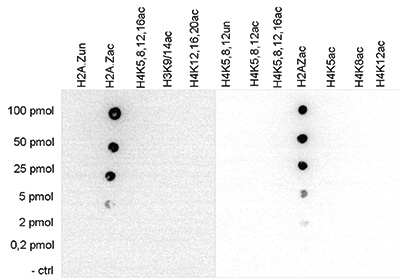
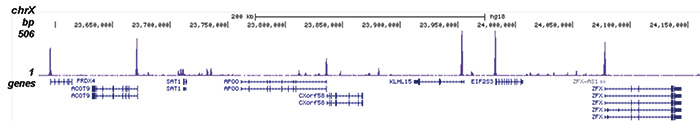 Figure 4. Cross reactivity test using the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac
Figure 4. Cross reactivity test using the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac A Dot Blot analysis was performed to test the cross reactivity of the Diagenode antibody against H2A.Zac (Cat. No. pAb-173- 050) with peptides containing other histone acetylations and the unmodified H2A.Z sequence. One hundred to 0.2 pmol of the respective peptides were spotted on a membrane. The antibody was used at a dilution of 1:20,000. Figure 4 shows a high specificity of the antibody for the modification of interest.
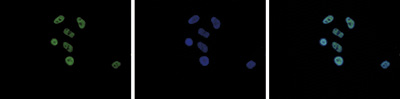
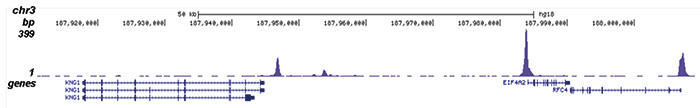 Figure 5. Immunofluorescence using the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac
Figure 5. Immunofluorescence using the Diagenode antibody directed against H2A.Zac HeLa cells were stained with the Diagenode antibody against H2A.Zac (cat. No. pAb-173-050) and with DAPI. Cells were fixed with 4% formaldehyde for 10’ and blocked with PBS/TX-100 containing 5% normal goat serum and 1% BSA. The cells were immunofluorescently labelled with the H2A.Zac antibody (left) diluted 1:500 in blocking solution followed by an anti-rabbit antibody conjugated to Alexa488. The middle panel shows staining of the nuclei with DAPI. A merge of the two stainings is shown on the right.